- Main Page
- A1C Test
- Advance Directives
- Anxiety
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Aphrodisiacs
- Apple Cider Vinegar
- Arrhythmia
- Atrial Fibrillation - AFib
- Back Pain
- Blood Tests
- Blood Test Tubes
- Blood Types
- BMI Calculator
- Body Mass Index - BMI
- Bone Density Scan
- Bone Scan
- BPPV
- Bronchitis
- Cancer - Lung
- Carbohydrates
- Cardiac Catheterization
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Caregiver Glossary
- Caregiver Resources - LGBTQ+
- Caregiver Resources - MO
- Caregiver Resources - USA
- Continuous Glucose Monitors
- Cholesterol
- Citalopram
- COPD
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Cough
- CPAP
- CT scan
- Cyclobenzaprine
- Degenerative Disc Disease
- Depression
- Diabetes Information
- Diabetes - Type 1
- Diabetes - Type 2
- Diabetes - Type 3c
- Diabetes Facts
- Diabetes Care
- Diabetes Care Team
- Diabetes & Fruits
- Diabetes - Gestational
- Diabetes - Pre
- Diabetic Terms
- Diabetes & Vegetables
- Diet - Boiled Egg
- Diet - DASH
- Diet - Fat Burning
- Diet - Mediterranean
- Diet - Military
- Disability
- Disability Permits
- Do Not Resuscitate
- Dupixent®
- Echocardiogram
- E-Cigarettes
- Electrocardiogram
- Electromyography
- Emphysema
- Epidural - Lumbar
- Epidural - Transforaminal
- Epsom Salt
- Facet Arthropathy
- Farxiga®
- Flu - Influenza
- Fluoroscopy
- Gabapentin
- GERD
- Glycemic Index
- Gout
- Headaches
- Healing & Energy Work
- Health Facts
- Health Info. Lines
- Heart Attack
- Heart Disease - Other
- Heart Failure
- Heart Imaging Tests
- Herbal Terms
- Herbal Medicine
- Herb & Oils Uses
- Herniated disk
- HIPAA
- Home Remedies
- Humalog®
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Hyperglycemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hyperlipidemia
- Hypertension
- Hypoglycemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypotension
- Important Numbers
- Indomethacin
- Informed Consent
- Inhalers
- Insomnia
- Insulin
- Juice Fasting
- Juice Recipes
- Kidney Cysts
- Kidney Disease
- Lantus®
- Lemon Benefits
- Lime Benefits
- Liver Disease
- Lumbar Retrolisthesis
- Medicaid
- Medical Specialties
- Medicare
- Medicare - Your Rights
- Melatonin
- Men's Health
- Mental Health
- MO HealthNet
- Mounjaro®
- MRI Scan
- Myelography
- Naproxen
- Nasal Polyps
- Nuclear Medicine
- Nutrition - Adults
- Nutrition - Adults, Older
- Nutrition - Kids
- Obesity
- Otolaryngologist
- Oxycodone-Acetaminophen
- Pain Management
- Peripheral Artery Disease
- Parking Spaces
- PET/CT Scan
- PET Scan
- Potassium
- Prescription Drugs
- Prurigo Nodularis
- PVC's
- Quetiapine
- Quit Smoking
- Radiculopathy
- Red Yeast Rice
- Reiki
- Salt & Sodium
- Salt Water Flush
- Sciatica
- Service Animals
- Sleep Apnea
- Sleep Disorders
- Sleep Studies
- SPECT Scan
- Spinal Stenosis
- Statins
- Stents
- Stress Test - Exercise
- Stress Test - Nuclear
- Sugars - Sweeteners
- Support Groups
- Tardive Dyskinesia
- Testosterone
- Trazodone
- Ultrasound
- Vaccines 19 and up
- Vaccines by Age
- Vaccines 0-6 yrs
- Vaccines 7-18 yrs
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Vertigo
- Vital Records
- Vital Signs
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin F
- Vitamin K
- Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamins Recommended
- Water Benefits
- X-Rays
Needed to read PDF's
Ultrasound
Overview
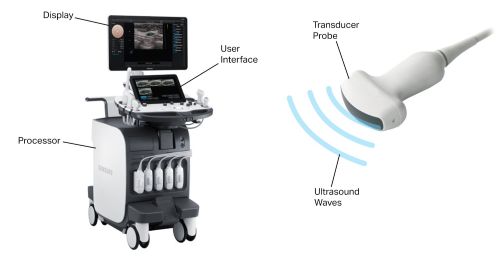
Ultrasound is a non-invasive way to see inside the body. It uses sound waves to create images in real-time. This helps doctors and patients understand what’s going on inside.
Ultrasound is used in many ways in medicine. It helps check on babies during pregnancy and looks at blood flow. It also checks for problems in muscles, guides procedures, and finds issues in organs like the liver and thyroid.
Ultrasound is safe because it doesn’t use harmful radiation. It lets doctors see how organs move and work. This helps them make better diagnoses and treatment plans.
Ultrasound technology keeps getting better. It now has clearer images, 3D and 4D views, and better contrast agents. This article will explore how ultrasound works, its uses, and its big impact on healthcare.
What is an Ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a non-invasive way to see inside the body. It uses sound waves to create images. This technology is key for diagnosing and monitoring health, and for guiding medical procedures.
Definition of Ultrasound
Ultrasound, or sonography, uses sound waves beyond what we can hear. A transducer, a small device on the skin, sends out these waves. The waves bounce off body parts, creating echoes that the transducer catches.
How Ultrasound Works
The transducer has special crystals that turn electrical energy into sound waves. When placed on the skin with gel, it sends sound waves into the body. These waves hit different parts of the body, bouncing back at different speeds and strengths.
The echoes from these waves are turned into images by the ultrasound machine. The gel helps by getting rid of air pockets, making sure the sound waves can travel well.
| Ultrasound Component | Function |
| Transducer | Emits and receives high-frequency sound waves |
| Sound waves | Travel through the body and create echoes |
| Ultrasound gel | Facilitates transmission of sound waves between transducer and skin |
| Echoes | Reflected sound waves processed to create images |
Ultrasound is safe because it doesn’t use harmful radiation. It’s great for checking on a baby during pregnancy and for looking at organs, blood vessels, and soft tissues in the body.
Types of Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound technology is used in many medical tests. It uses sound waves to see inside the body. This helps doctors check different parts of the body. Here are some common ultrasound tests:
Abdominal Ultrasound
An abdominal ultrasound looks at organs in the belly. It checks the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys. It can find problems like tumors and stones. It also checks how well organs work and blood flow.
Pelvic Ultrasound
A pelvic ultrasound looks at the reproductive organs. For women, it checks the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. For men, it looks at the prostate gland and bladder. It helps find issues like cysts and fibroids.
Obstetric Ultrasound
Obstetric ultrasounds are for pregnant women. They check how the baby is growing and if there are any problems. They can even show if the baby is a boy or girl. These ultrasounds are important during pregnancy.
| Trimester | Ultrasound Purpose |
| First (Weeks 1-12) | Confirm pregnancy, determine gestational age, assess viability |
| Second (Weeks 13-27) | Examine fetal anatomy, screen for abnormalities, determine gender |
| Third (Weeks 28-40) | Monitor fetal growth, position, and well-being |
Breast Ultrasound
Breast ultrasounds check for problems in the breast. They can find things that mammograms can’t. They help figure out if a lump is a cyst or a tumor.
Vascular Ultrasound
Vascular ultrasounds look at blood flow in veins and arteries. They help find problems like blood clots and narrowed arteries. They use Doppler technology to see how blood moves.
Why it's done
Ultrasound is used for many reasons, including to:
- View the uterus and ovaries during pregnancy and monitor the developing baby's health.
- Diagnose gallbladder disease.
- Evaluate blood flow.
- Guide a needle for biopsy or tumor treatment.
- Examine a breast lump.
- Check the thyroid gland.
- Find genital and prostate problems.
- Assess joint inflammation, called synovitis.
- Evaluate metabolic bone disease.
2D vs. 3D vs. 4D ultrasound?
For ultrasounds during pregnancy, the traditional ultrasound is a two-dimensional (2D) image of the fetus. 2D ultrasound produces outlines and flat-looking images, which allows your healthcare provider to see the fetus's internal organs and structures.
Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound allows the visualization of some facial features of the fetus and possibly other body parts such as fingers and toes. Four-dimensional (4D) ultrasound is 3D ultrasound in motion. Providers rarely use 3D or 4D fetal ultrasound imaging for medical purposes, though it can be useful in diagnosing a facial or skeletal issue. They do, however, use 3D ultrasound for other medical purposes, such as evaluating uterine polyps and fibroids.
While ultrasound is generally considered to be safe with very low risks, the risks may increase with unnecessary prolonged exposure to ultrasound energy or when untrained users operate an ultrasound machine. Because of this, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advises against getting a 3D ultrasound for non-medical reasons such as for “keepsake” moments or entertainment.
Advancements in Ultrasound Technology
Ultrasound imaging has made big strides in recent years. It now gives doctors more detailed and accurate info. These new techs have boosted ultrasound’s role in many medical fields, leading to better patient care and results.
3D and 4D Ultrasound
3D ultrasound makes three-dimensional images of what’s inside. This is super helpful in prenatal care, letting parents see their baby in detail. 4D ultrasound adds time to these images, showing the baby moving in real-time.
Doppler Ultrasound
Doppler ultrasound measures blood flow in vessels. It works by detecting sound wave changes from moving blood cells. This helps spot conditions like blood clots and narrowed arteries.
| Condition | Diagnostic Value |
| Blood clots | Detects obstructions in blood vessels |
| Arterial stenosis | Identifies narrowing of arteries |
| Venous insufficiency | Assesses blood flow in veins |
Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) uses intravenous contrast agents to show blood flow better. These tiny gas-filled microbubbles make blood more visible on ultrasound. CEUS is great for checking organ blood flow, spotting lesions, and finding blood flow issues.
Benefits of Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging has many advantages that make it a key tool in healthcare. It’s non-invasive and shows what’s inside the body in real-time without harmful radiation. Let’s look at the main benefits of using ultrasound.
Non-invasive and Safe
One big plus of ultrasound is that it doesn’t hurt and doesn’t use harmful radiation. This makes it safe for pregnant women and kids. It’s also painless and has no side effects.
Real-time Imaging
Ultrasound lets doctors see how organs and blood vessels move and work. This is great for checking the heart and watching how a baby grows inside the womb. It also helps with procedures like biopsies.
Cost-effective
Ultrasound is cheaper than MRI Scans or CT Scans. It’s less expensive to buy and keep running. Plus, it’s faster, which saves money for both hospitals and patients.
The table below shows why ultrasound is so valuable:
| Benefit | Description |
| Non-invasive | Painless procedure with no ionizing radiation exposure |
| Real-time imaging | Dynamic visualization of organ movement and function |
| Cost-effective | Lower equipment and exam costs compared to other modalities |
| Widely available | Accessible in most healthcare facilities and can be performed at bedside |
| Versatile | Applicable for a wide range of diagnostic and interventional applications |
Ultrasound’s many benefits make it a key tool in healthcare. As technology gets better, ultrasound will likely become even more important for diagnosing and treating diseases.
Who performs an ultrasound?
A doctor or a healthcare provider called an ultrasound technician or sonographer performs ultrasounds. They’re specially trained to operate an ultrasound machine properly and safely.
It’s important to always have your ultrasound performed by a medical professional and in a medical facility.
How do I prepare for an ultrasound?
Getting ready for an ultrasound exam is key for a good experience. Your doctor will give you specific instructions for your ultrasound. But, there are some general tips that work for most exams.
One key thing is fasting. You might need to not eat or drink before the exam. This is often true for ultrasounds of the belly or pelvis. Food and drinks can mess up the images. Your doctor will tell you how long to fast, usually 4 to 8 hours.
| Type of Ultrasound | Fasting Requirements |
| Abdominal | 6-8 hours |
| Pelvic (female) | 4-6 hours |
| Obstetric | None |
| Breast | None |
When it comes to clothing, wear loose, comfy clothes. This makes it easier to get to the area being checked. You might need to change into a hospital gown for some exams. Also, leave jewelry and avoid lotions or powders on your skin. They can mess with the ultrasound gel.
Lastly, talk about your medical history and any meds you’re taking with your doctor. This helps the sonographer and radiologist understand the images better. Tell them about any surgeries, chronic conditions, or allergies that might be important for the exam.
What happens during an ultrasound?
A trained technician or doctor will guide you through the ultrasound process. You might need to change into a hospital gown and lie on a table.
The technician will put special ultrasound gel on the area to be checked. This gel removes air pockets for clearer images. Then, they place a small device called a transducer on your skin and move it over the area.
The transducer sends sound waves that bounce off your internal structures. These waves create real-time images on a computer screen. The technician might ask you to hold your breath or change positions for better views.
What to Expect During the Exam
You might feel slight pressure from the transducer as it moves. But the exam is usually painless and doesn’t hurt. The technician will take measurements and capture images for analysis.
Duration of the Exam
The time needed for an ultrasound exam varies. It depends on the type and area being checked. Here are some typical times:
| Ultrasound Type | Duration |
| Abdominal | 30-60 minutes |
| Pelvic | 30-60 minutes |
| Obstetric | 30-45 minutes |
| Breast | 15-30 minutes |
| Vascular | 30-90 minutes |
After the exam, the gel is wiped off, and you can go back to your day. A radiologist will look at the images and send a report to your doctor. Your doctor will then talk to you about the results and what to do next.
Ultrasound in Prenatal Care
Ultrasound is key in checking the health and growth of the fetus during pregnancy. Prenatal ultrasound exams let parents see their baby for the first time. They also give doctors important info on fetal development and any pregnancy complications.
Monitoring Fetal Development
Ultrasounds help doctors track the fetus’s growth. They can see how big the baby is, check on organs and limbs, and guess when the baby will be born. This helps make sure the pregnancy is going well and spots any problems early.
Detecting Possible Complications
Ultrasound is great for finding possible pregnancy problems. Some issues that might show up include:
| Condition | Description |
| Placental issues | Such as placenta previa or placental abruption |
| Fetal growth restriction | When the fetus is not growing at the expected rate |
| Congenital abnormalities | Such as heart defects or neural tube defects |
| Multiple pregnancies | Detecting twins, triplets, or higher-order multiples |
Finding problems early lets doctors plan the best care. This helps keep the mom and baby healthy.
Gender Determination
While not the main goal, many parents want to know their baby’s gender. Gender determination is usually clear at the mid-pregnancy ultrasound, between 18 and 22 weeks. But, the main focus of ultrasound is the health and well-being of the fetus.
Ultrasound-guided Procedures
Ultrasound technology has changed medicine a lot. It lets doctors do ultrasound-guided procedures more precisely and safely. These procedures use ultrasound images to guide needles or tools to the right spots in the body.
A biopsy is a common procedure. It involves taking a small tissue sample for lab tests. Ultrasound helps doctors aim for the right spot, avoiding damage to other tissues. This is really helpful for biopsies of hard-to-reach places like the liver or kidney.
Ultrasound is also used for injections. This includes shots for pain or to put medicine in joints or muscles. Doctors can see the needle’s path live, making sure it hits the right spot. This makes the treatment work better and is more comfortable for the patient.
Aspiration is another use of ultrasound-guided procedures. It’s for removing fluid or substances from the body. This is often done to drain cysts or excess fluid in organs. Ultrasound helps place the needle exactly, lowering the chance of harming nearby areas.
Ultrasound-guided procedures have many benefits. They are more accurate and have fewer risks. They also make procedures shorter, recovery faster, and outcomes better. As ultrasound tech gets better, we’ll see even more ways to help patients.
Are ultrasounds safe?
Yes, research to date has largely shown ultrasound technology to be safe with no harmful side effects. Ultrasound doesn’t use radiation, unlike some other medical imaging tests, such as X-rays and CT scans.
Diagnostic ultrasound is a safe procedure that uses low-power sound waves. There are no known risks.
Ultrasound is a valuable tool, but it has limitations. Sound waves don't travel well through air or bone. This means ultrasound isn't effective at imaging body parts that have gas in them or are hidden by bone, such as the lungs or head. Ultrasound also may not be able to see objects that are located very deep in the human body.
To view these areas, your healthcare professional may order other imaging tests, such as CT Scan or MRI Scan or X-rays.
Results
When should I know the results of my ultrasound?
The time it takes to get your results depends on the type of ultrasound you get. In some cases, such as prenatal ultrasound, your provider may analyze the images and provide results during the test.
In other cases, a radiologist, a healthcare provider trained to supervise and interpret radiology exams, will analyze the images and then send the report to the provider who requested the exam. Your provider will then share the results with you or they may be available in your electronic medical record (if you have an account set up) before your provider reviews the results.
What conditions can be detected by ultrasound?
Ultrasound can help providers diagnose a wide range of medical issues, including:
- Abnormal growths, such as tumors or cancer.
- Blood clots.
- Enlarged spleen.
- Ectopic pregnancy (when a fertilized egg implants outside of your uterus).
- Gallstones.
- Aortic aneurysm.
- Kidney or bladder stones.
- Cholecystitis (gallbladder inflammation).
- Varicocele (enlarged veins in the testicles).
What questions should I ask my healthcare provider?
If you need an ultrasound, you may want to ask your provider the following questions:
- What type of ultrasound do I need?
- What should I do to prepare for my ultrasound?
- Do I need any other tests?
- When should I expect to get test results?
How Much Does an Ultrasound Cost?
The cost of your ultrasound depends on where you live and the type of scan you get. Generally, a pregnancy ultrasound can cost as little as $200 up to $1,000 or more. Most insurance companies cover the cost of prenatal ultrasounds, and you should check with your insurer for out-of-pocket costs for other types of ultrasounds.
FAQ's
Q: What is ultrasound?
A: Ultrasound is a non-invasive way to see inside the body. It uses sound waves to create images in real-time. It’s used in many medical areas, like checking on babies during pregnancy and looking at blood vessels.
Q: How does ultrasound work?
A: Ultrasound uses a special tool to send and get sound waves. These waves bounce off body tissues and create images. A gel is used on the skin to help the sound waves move better.
Q: What are the different types of ultrasound examinations?
A: There are many types of ultrasound exams. These include looking at the belly, pelvic area, and checking on babies. There’s also ultrasound for the breasts and blood vessels. Each exam looks at different parts of the body to find and check on health issues.
Q: How should I prepare for an ultrasound exam?
A: Getting ready for an ultrasound can vary. Your doctor will tell you what to do. This might include not eating before, wearing loose clothes, and talking about your health and medicines.
Q: What happens during an ultrasound procedure?
A: During an ultrasound, a technician will put gel on your skin. They will then move a tool over the area being checked. This tool sends sound waves and catches the echoes to make images. How long it takes depends on the type of ultrasound.
Q: Is ultrasound imaging safe?
A: Yes, ultrasound is safe. It doesn’t hurt and doesn’t use harmful radiation. It’s also good because it shows images in real-time and is cheaper than other ways to see inside the body.
Q: How is ultrasound used in prenatal care?
A: Ultrasound is key in prenatal care. It lets doctors check on the baby’s growth and health. It can also show if there are any problems and if the baby is a boy or girl. Regular checks help keep the mom and baby safe and healthy.
Q: What are some of the latest advancements in ultrasound technology?
A: New ultrasound tech includes 3D and 4D images, which are more detailed. There’s also Doppler ultrasound for blood flow and contrast-enhanced ultrasound for clearer images. These advancements help doctors make better diagnoses.
Q: What is the role of ultrasound in guided medical procedures?
A: Ultrasound helps guide medical procedures like biopsies and injections. It makes these procedures more precise and safer. It also makes patients more comfortable during the process.
Q: What training and certification are required for sonographers?
A: Sonographers need to finish a program in diagnostic medical sonography. This includes classes and hands-on training. After that, they can get certified by groups like the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). They must keep learning to stay up-to-date with new ultrasound methods.
One Final Note..
An ultrasound is a test that takes images inside your body. The test uses high-frequency sound waves to create pictures in real time of organs and soft tissue. Not just a tool during pregnancy, an ultrasound can be used to examine your kidneys, breasts, vascular system, thyroid gland, and pelvic organs.
Ultrasounds are common, safe and effective imaging tests. Make sure you get an ultrasound from a well-trained professional (sonographer) who understands how to use this technology properly. If you have any questions about your specific ultrasound test, talk to your healthcare provider. They’re available to help.
Find me on Social Media
 |
Don't forget to bookmark me to see updates.. Copyright © 2000 - 2025 - K. Kerr Most recent revision February 09, 2026 07:37:13 AM
|











