- Main Page
- A1C Test
- Aliens
- American Flag
- Annuals
- Anxiety
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Apple Cider Vinegar
- Arrhythmia
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Avoiding Scams
- Awareness Ribbons
- Bamboo
- Banana Tree, Grand Nain
- Banana Tree, Ice Cream
- Banana Tree, Zebrina Rojo
- Beekeeping
- Benign P P Vertigo
- Birthday on Planets
- Birth Month
- Blood Pressure - High
- Blood Pressure - Low
- Blood Tests
- Body Mass Index - BMI
- BMI Calculator
- Boogaloo
- Bookmarks
- Boot Anatomy
- Boot Fit Guide
- Boot Glossary
- Boot Leathers
- Boot Makers
- Boot Retailers
- Boot Styles - Western
- Boot Toes & Heels - Western
- Boot Toes & Heels - Work
- Bronchitis
- Candle Colors
- Carbohydrates
- Cardiac Catheterization
- CGM's
- Chakras
- Chinese Zodiac
- Cholesterol
- Christmas Tree
- Color Codes Chart
- C.O.P.D.
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Country Stars
- Cowboy Hat Etiquette
- Cowboy Hat Sizing
- C.P.A.P.
- Credit Score Checkers
- Crystals & Gems
- CT scan
- Degenerative Disk Disease
- Depression
- Diabetes Info.
- Diabetes - Pre
- Diabetes - Type 1
- Diabetes - Type 2
- Diabetes - Type 3c
- Diabetes - Gestational
- Diabetes Care
- Diabetes Care Team
- Diabetes Terms
- Diabetes Treatment
- Diabetes & Fruits
- Diabetes & Veg's
- Diet - Boiled Egg
- Diet - DASH
- Diet - Fat Burning
- Diet - Mediterranean
- Diet - Military
- Disability
- Dream Catchers
- Dupixent®
- Echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram
- Emphysema
- Epsom Salt
- Eye Teasers
- Fairies
- Farxiga®
- Flower Astrology
- Fonts
- Foods To Regrow
- Friend
- Funny Things
- Fun Stuff
- Glycemic Index
- Gout
- Growing Blueberries
- Halloween
- Halloween Treats
- Headaches
- Health Info. Lines
- Heart Attack
- Heart Disease - Other
- Heart Failure
- Heart Tests
- Hello!!
- Herbal Codes
- Herbology
- Herb & Oils Uses
- Herniated disk
- Home Remedies
- House Plants
- Humalog®
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypokalemia
- Important Numbers
- Insomnia
- Insulin
- Juice Recipes
- Karma
- Kidney Cysts
- Kidney Disease
- Kinds of Tea
- Lantus®
- Lemon Cleanse
- Logger vs Lineman Boots
- Macaroni!!
- Medicare
- Mental Health
- MO HealthNet
- Moon Phases
- Motorcycle Manufacturers
- Mounjaro®
- MRI Scan
- My Athletic Shoes
- My Boots & Spurs
- My Cowboy Hats
- Myelography
- Mystical Unicorn
- Nasal Polyps
- Natal Astrology Chart
- Never Forget
- Nuclear Medicine
- Obesity
- One Little Rose
- Orchid Growing
- Orchid Sources
- Pagan Humor
- Pagans vs.Wiccans
- Parking Spaces
- PayPal.Me
- Pentagram vs. Pentacle
- Perennials
- Peripheral Artery Disease
- Phobias A-Z
- Plant Care
- Plant Zone Map
- Potassium
- Propagating Plants
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Psychic Gifts
- PVC's
- Quit Smoking
- Recipes I like
- Red Yeast Rice
- Roses
- Runes
- Sadie & Beethoven
- Salt & Sodium
- Salt Water Flush
- Sciatica
- Service Animals
- Shape Shifters
- Sleep Apnea
- Sleep Disorders
- Sleep Studies
- Smile
- Speed Test
- Spices You Need
- Spices I Have
- Spinal Stenosis
- Stents
- Steel Toe vs. Comp. Toe
- Stress Test - Exercise
- Stress Test - Nuclear
- Superstitions
- Symbols
- Tarot
- The Ten Commandments
- Tools of the Craft
- Top Expensive Movies
- Top Modern Westerns
- Top 100 Westerns
- Toyota Yaris 2008
- Toyota Yaris 2012
- Tree, Calamondin Orange
- Tree, Lemon (Meyer)
- Tree, Lime
- Tree Signs
- Ultrasound
- US Bill of Rights
- US Constitution
- US Declaration of Independence
- Vaccines by Age
- Vaccines - Adults
- Vaccines - Kids
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Vertigo
- Vital Records
- Vital Signs
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- Vitamins & Minerals
- Water Therapy
- Wiccan Rede
- X-rays
- Yin / Yang
- Zodiac Signs
Heart Disease
Key points
- Coronary artery disease is the most common type of heart disease.
- There are many other conditions that affect the heart.
- The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions.
- Know your risk for heart disease so you can prevent it.
- High blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking are key risk factors.
- About 1 in 5 people in the United States died from heart disease in 2022.
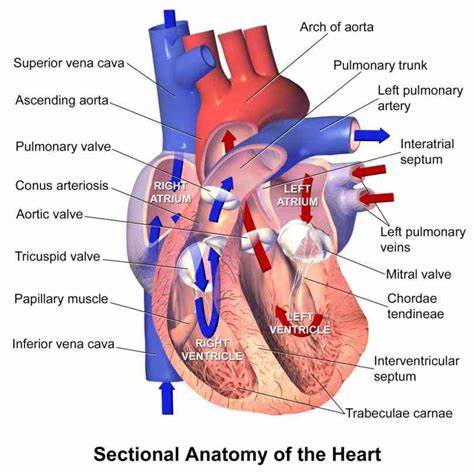
What is heart disease?
The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type of heart disease in the United States is coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD affects the blood flow to the heart. Decreased blood flow can cause a heart attack.
Symptoms
Sometimes heart disease may be "silent" and not diagnosed until a person experiences signs or symptoms of a heart attack, heart failure, or an arrhythmia. When these events happen, symptoms may include:
- Heart attack: Chest pain or discomfort, upper back or neck pain, heartburn, nausea or vomiting, extreme fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
- Arrhythmia: Fluttering feelings in the chest (palpitations).
- Heart failure: Shortness of breath, fatigue, or swelling of the feet, ankles, legs, abdomen, or neck veins.
Risk factors
Americans at risk for heart disease
High blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking are key risk factors for heart disease.
Several other medical conditions and lifestyle choices can also put people at a higher risk for heart disease, including:
- Diabetes
- Overweight and obesity
- Unhealthy diet
- Physical inactivity
- Excessive alcohol use
Conditions related to heart disease
Coronary artery disease, also called Coronary Heart Disease or ischemic heart disease, is the most common type of heart disease, but there are many other conditions that affect the heart.
Acute coronary syndrome is a term that includes heart attack and unstable angina.
Angina, a symptom of coronary artery disease, is chest pain or discomfort that happens when the heart muscle is not getting enough blood. Angina may feel like pressure or a squeezing pain in the chest. The pain also may occur in the shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back. It may feel like indigestion.
There are two forms of angina—stable or unstable:
- Stable angina happens during physical activity or under mental or emotional stress.
- Unstable angina is chest pain that occurs even while at rest, without apparent reason. This type of angina is a medical emergency.
Aortic aneurysm and dissection are conditions that can affect the aorta, the major artery that carries blood from the heart to the body. An aneurysm is an enlargement in the aorta that can rupture or burst. A dissection is a tear in the aorta, which is a medical emergency. For more information, see the aortic aneurysm information page.
Arrhythmias are irregular or unusually fast or slow heartbeats. Arrhythmias can be serious. One example is called ventricular fibrillation. This type of arrhythmia causes an abnormal heart rhythm that leads to death unless treated right away with an electrical shock to the heart (called defibrillation). Other arrhythmias are less severe but can develop into more serious conditions, such as atrial fibrillation, which can cause a stroke. see the arrhythmias information page
Atherosclerosis happens when plaque builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart (called coronary arteries). Plaque is made up of cholesterol deposits. Plaque buildup causes arteries to narrow over time.
Atrial fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia that can cause rapid, irregular beating of the heart's upper chambers. Blood may pool and clot inside the heart, increasing the risk for heart attack and stroke. For more information, see the atrial fibrillation information page.
Cardiomyopathy happens when the heart muscle becomes enlarged or stiff. This can lead to inadequate heart pumping (or weak heart pump) or other problems. Cardiomyopathy has many causes, including family history of the disease, prior heart attacks, uncontrolled high blood pressure, and viral or bacterial infections.
Congenital heart defects are problems with the heart that are present at birth. They are the most common type of major birth defect. Examples include abnormal heart valves or holes in the heart's walls that divide the heart's chambers. Congenital heart defects range from minor to severe.
Heart failure is often called congestive heart failure because of fluid buildup in the lungs, liver, legs, and feet. Heart failure is a serious condition that occurs when the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It does not mean that the heart has stopped but that muscle is too weak to pump enough blood. Most of heart failure cases are chronic, or long-term heart failures. The only cure for heart failure is a heart transplant. However, heart failure can be managed with medications or medical procedures. For more information, see the heart failure information page.
Marfan syndrome. Marfan syndrome is a genetic condition that affects connective tissue, which provides support for the body and organs. It can damage the blood vessels, heart, eyes, skin, lungs, and the bones of the hips, spine, feet, and rib cage.
Mental health disorders can be short- or long-term and can interfere with a person's mood, behavior, thinking, and ability to relate to others. Various studies have shown the impact of trauma, depression, anxiety, and stress on the body, including stress on the heart. see the mental health information page.
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) happens when the arteries that supply blood to the arms and legs (the periphery) become narrow or stiff. PAD usually results from atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque and narrowing of the arteries. With this condition, blood flow and oxygen to the arm and leg muscles are low or even fully blocked. Signs and symptoms include leg, calf, buttock, hip, or thigh pain, and numbness in the feet. see the Peripheral arterial disease information page
Pulmonary hypertension happens when the pressure in the arteries leading from the heart to the lungs is too high. There are many conditions that lead to pulmonary hypertension, including connective tissue disease, liver disease, emphysema, and chronic blood clots in the lungs. Symptoms of pulmonary hypertension include shortness of breath and fatigue.
Rheumatic heart disease is a complication of rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever can develop after a sore throat caused by streptococcal bacteria. The infection can cause damage to the heart valves.
Valvular heart disease. Healthy heart valves can fully open and close during a heartbeat, but diseased valves cannot. If the heart valves are diseased, the heart can't effectively pump blood throughout the body and must work harder to pump. This can lead to heart failure, sudden cardiac arrest (when the heart stops beating), heart palpitations (rapid, fluttering, or pounding), shortness of breath, or swelling in your legs and feet.
Diagnosis
To diagnose heart disease, a healthcare professional examines you and listens to your heart. You are usually asked questions about your symptoms and your personal and family medical history.
Tests
Many different tests are used to diagnose heart disease.
- Blood tests. Certain heart proteins slowly leak into the blood after heart damage from a heart attack. Blood tests can be done to check for these proteins. A high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) test checks for a protein linked to inflammation of the arteries. Other blood tests may be done to check cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
- Chest X-ray. A chest X-ray shows the condition of the lungs. It can show if the heart is enlarged.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). An ECG is a quick and painless test that records the electrical signals in the heart. It can tell if the heart is beating too fast or too slow.
- Holter monitoring. A Holter monitor is a portable ECG device that's worn for a day or more to record the heart's activity during daily activities. This test can detect irregular heartbeats that aren't found during a regular ECG exam.
- Echocardiogram. This noninvasive exam uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart in motion. It shows how blood moves through the heart and heart valves. An echocardiogram can help determine if a valve is narrowed or leaking.
- Exercise tests or stress tests. These tests often involve walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike while the heart is checked. Exercise tests help reveal how the heart responds to physical activity and whether heart disease symptoms occur during exercise. If you can't exercise, you might be given medicine that affects the heart like exercise does.
- Cardiac catheterization. This test can show blockages in the heart arteries. A long, thin flexible tube called a catheter is inserted in a blood vessel, usually in the groin or wrist, and guided to the heart. Dye flows through the catheter to arteries in the heart. The dye helps the arteries show up more clearly on X-ray images taken during the test.
- Heart CT scan, also called cardiac CT scan. In a cardiac CT scan, you lie on a table inside a doughnut-shaped machine. An X-ray tube inside the machine rotates around your body and collects images of your heart and chest.
- Heart magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. A cardiac MRI uses a magnetic field and computer-generated radio waves to create detailed images of the heart.
Treatment and recovery
Heart disease treatment depends on the cause and type of heart damage. Treatment for heart disease may include:
- Lifestyle changes such as eating a diet low in salt and saturated fat, getting more exercise, and not smoking.
- Medicines.
- A heart procedure.
- Heart surgery.
Medications
You may need medicines to control heart disease symptoms and prevent complications. The type of medicine used depends on the type of heart disease.
Surgery or other procedures
Some people with heart disease may need a heart procedure or surgery. The type of treatment depends on the type of heart disease and how much damage has happened to the heart.
What is cardiac rehabilitation?
Cardiac rehabilitation is an important program for anyone recovering from a heart attack. This can also include heart failure, or some types of heart surgery.
Cardiac rehabilitation is a supervised program that includes
- Physical activity.
- Education about healthy eating.
- Taking medicine as prescribed.
- Ways to help you quit smoking.
- Counseling to find ways to relieve stress and improve mental health.
A team of people may help you through cardiac rehabilitation.
This may include
- Your health care team.
- Exercise and nutrition specialists.
- Physical therapists.
- Counselors or mental health professionals.
Heart Disease Facts
Heart disease in the United States
In the United States:
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men, women, and people of most racial and ethnic groups.
- One person dies every 33 seconds from cardiovascular disease.
- In 2022, 702,880 people died from heart disease. That's the equivalent of 1 in every 5 deaths.
- Heart disease cost about $252.2 billion from 2019 to 2020. This includes the cost of health care services, medicines, and lost productivity due to death.
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Coronary heart disease is the most common type of heart disease. It killed 371,506 people in 2022.
- About 1 in 20 adults age 20 and older have CAD (about 5%).
- In 2022, about 1 out of every 5 deaths from cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) was among adults younger than 65 years old.
Heart attack
- In the United States, someone has a heart attack every 40 seconds.
- Every year, about 805,000 people in the United States have a heart attack. Of these, 605,000 are a first heart attack, and 200,000 happen to be people who have already had a heart attack.
- About 1 in 5 heart attacks are silent—the damage is done, but the person is not aware of it.
Did you know?
Early action is important for heart attack. Know the warning signs and symptoms of a heart attack.
As plaque builds up in the arteries of a person with heart disease, the inside of the arteries begins to narrow, which lessens or blocks the flow of blood.
Who is affected
Heart disease deaths vary by sex, race, and ethnicity
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for people of most racial and ethnic groups in the United States. These include African American, American Indian, Alaska Native, Hispanic, and White men. For women from the Pacific Islands and Asian American, American Indian, Alaska Native, and Hispanic women, heart disease is second only to cancer.
Below are the percentages of all deaths caused by heart disease in 2021, listed by ethnicity, race, and sex.
| Race or Ethnic Group | % of Deaths |
|
American Indian or Alaska Native |
15.5 |
| Asian | 18.6 |
| Black (Non-Hispanic) | 22.6 |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 18.3 |
| White (Non-Hispanic) | 18.0 |
| Hispanic | 11.9 |
| All | 17.4 |
Find me on Social Media
 |
Don't forget to bookmark my site to see updates.. Copyright © 2000 - 2025 K.
Kerr |






